In previous blog titled “What is PLC Programming?”, MODBUS PROTOCOL Blocks and MODBUS RTU MODBUS Master and MODBUS RTU Slave connection and programming in Mikrodev MP110 and MP211 PLC Series devices are discussed and analyzed. In order to define the processes comprehensively, in this blog post we will discuss MODBUS TCP protocols and blocks, within the frame of TCP Master and TCP Slave connection features and sample applications in MODBUS Protocols in Mikrodev MP110 and MP211 PLC Series devices.
Communication protocols between PLCs are server-client based, enabling interaction between different devices. MODBUS protocol, which is widely preferred in the automation industry, is preferred for serial communication with its simple and effective structure. It is also known as one of the oldest serial communication protocols that meet industrial communication needs.
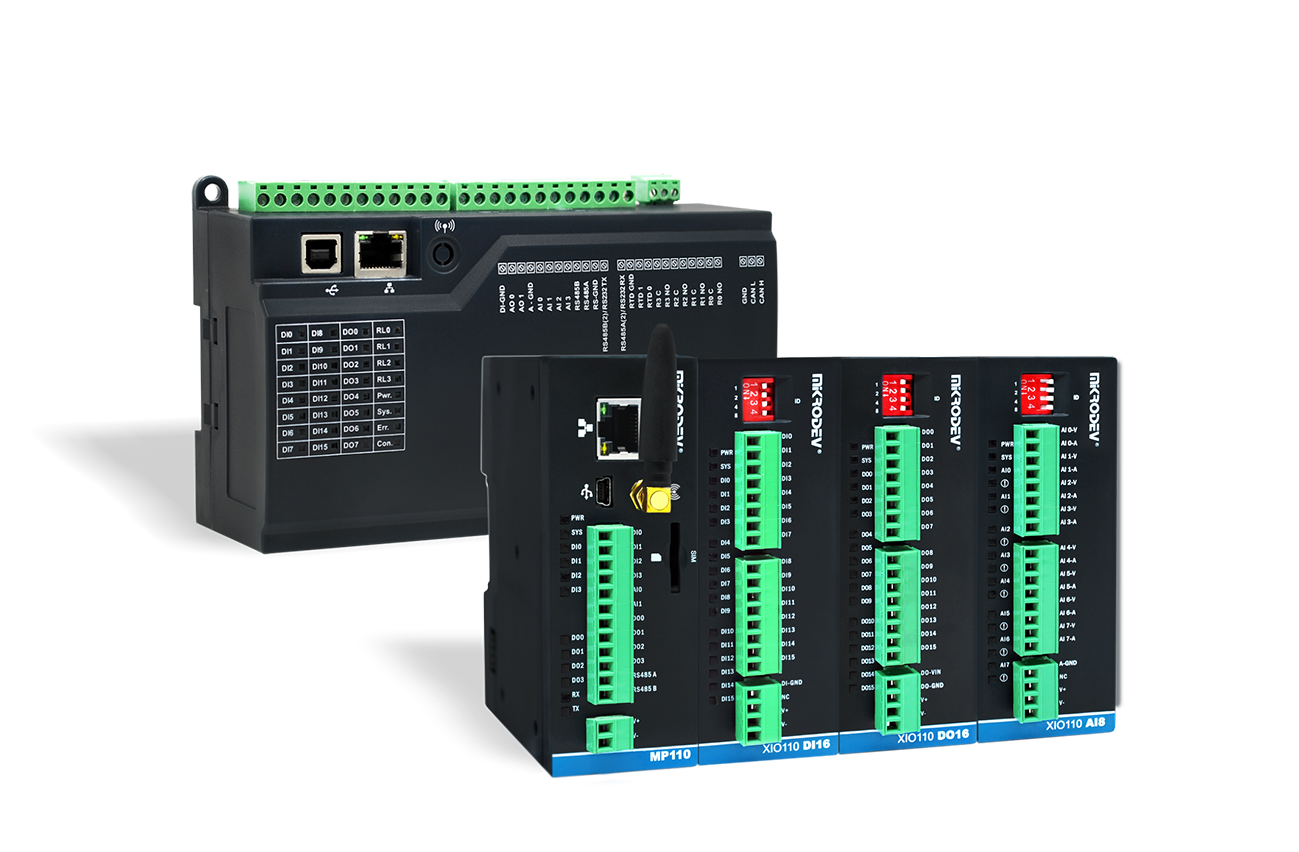
Mikrodev MP110 Series (Micro Level Controller) and MP211 Series (Medium and Large Level Controller) MODBUS TCP Master and MODBUS TCP Slave
MODBUS TCP Protocol Master
Connections
Connection explanations
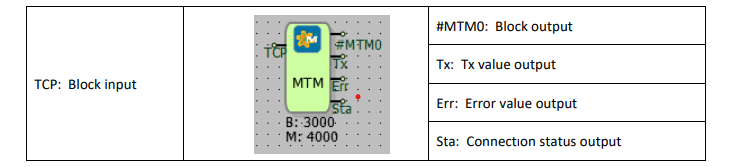
TCP: Block input
The block input connection to which the communication port is connected.
#MTM0: Block output
The block output connection.
Tx: Tx value output
It is the output connection which indicates the number of requests sent
Err: Number of errors in submitted requests
It is the output connection which indicates the error count of the sent requests
Sta: Connection status output
Indicates if the last executed request is successful or not.
Custom Settings
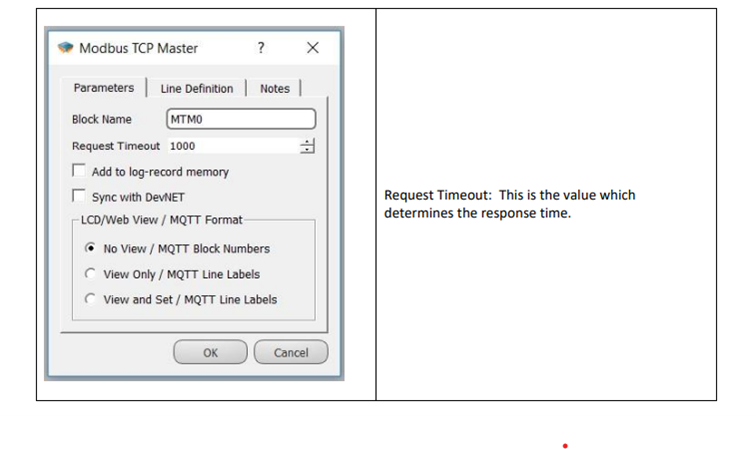
The MODBUS TCP Master block enables the Master MODBUS TCP protocol on the physical interface connected via the communication port input. The MODBUS TCP Master block is used to read or assign values over the MODBUS communication protocol. The activated protocol is finalized by connecting the request sending blocks to the MODBUS TCP Master block. In the MODBUS protocol, requests can usually be categorized as read or write. The MODBUS TCP Master block works in an integrated manner with the TCP Socket Block and MODBUS Word Reader / MODBUS Word Printer Blocks.
When MODBUS request blocks are triggered to read or write, these requests are added to the request queue in the MODBUS TCP Master block. Requests waiting in the queue in the MODBUS TCP Master block are pulled in sequence if the communication line is free, sent to the line and wait for a response. If a response is received within the timeout period, the received response is processed; if not, the request is canceled and the error counter is incremented by one. This waiting time is set in the special settings section of the MODBUS TCP Master block.
MODBUS messages are instant read or write requests and do not contain timestamp information. Therefore, the request queue in the MODBUS TCP Master block is organized with intelligent mechanisms to store read and write requests to the same point only in the last added request queue. During online monitoring, the “MODBUS Slave” utility is used to view values or assign new values via the MODBUS communication protocol.
Sample Application
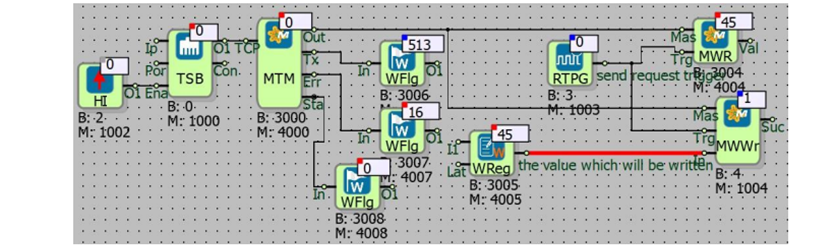
For example; Master MODBUS TCP protocol is activated via TCP socket block. The TCP Socket Block is designated as a requester. The device, as MODBUS TCP Master, transmits read and write requests to slave devices on the communication line. It is necessary to connect the output of the MODBUS TCP Master block to the corresponding “Efe” inputs of the MODBUS Reader / Writer blocks. MODBUS Slave utility is used to read or write values with MODBUS. The values sent by the utility are read from the MODBUS Reader / Writer blocks. Word flags connected to the “Tx” and “Err” outputs of the MODBUS TCP Master block are used to read the number of requests sent and the number of errors in the requests. If the last data packet was successfully transmitted/received, the “Sta” output is 0; otherwise it is 1.
MODBUS TCP Protocol – Slave
Connections
Connection explanations
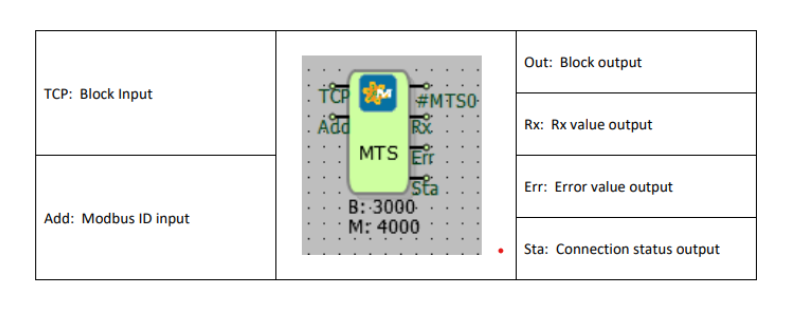
TCP: Block input
The block input connection to which communication port is connected
Add: Modbus ID input
Used to identify the Modbus ID address externally
Out: Block output
The output connection of the block
Rx: Rx value output
It is the output connection which indicates the number of requests sent.
Err: Error value output
It is the output connection which indicates the error count of the requests sent.
Sta: Connection status output
Indicates the success state of the last executed request.
Custom Settings
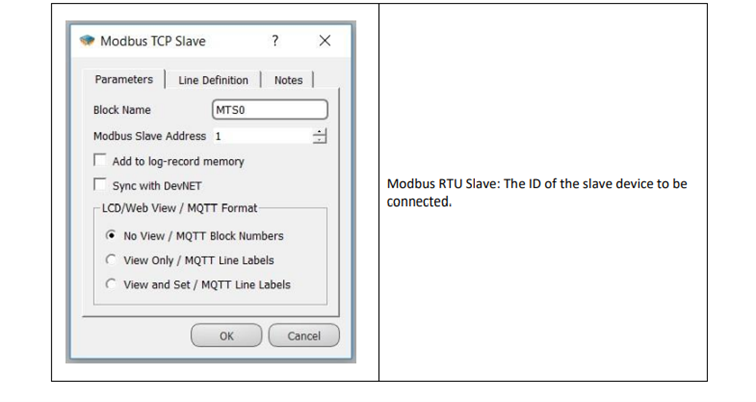
Block Explanation
The MODBUS TCP Slave block enables the MODBUS Slave protocol on the physical interface via the communication port input. It is used to read values from the program via MODBUS communication protocol. The output of the TCP Socket block is connected to the “TCP” input of the MODBUS TCP Slave block. The activated MODBUS TCP Slave device responds to requests from the designated communication port with its own MODBUS Identification Number (ID). The MODBUS Poll utility is used to see the sent values during online monitoring.
The blocks in the entire logic project and the MODBUS addresses in the variable address table will be accessed as determined by these channel and protocol settings.
Sample Application
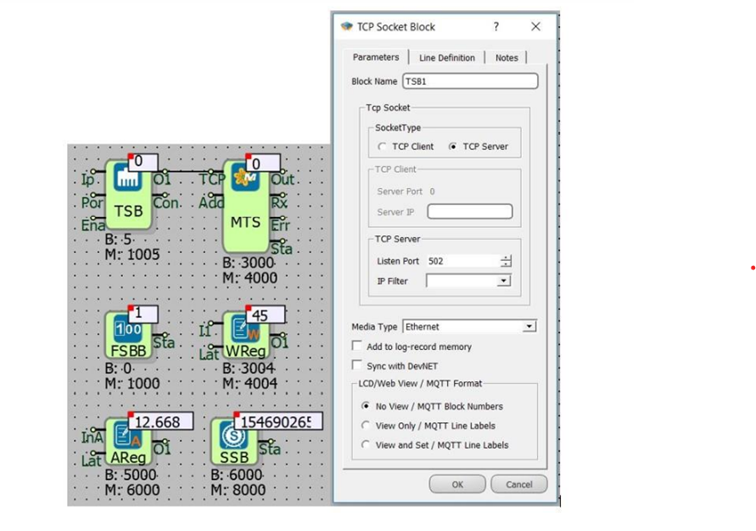
TCP Socket Block is preferred as a server. The MODBUS TCP Slave block works in server mode where the device is programmed by connecting to the TCP Socket block output. (The connection type is Ethernet.) The MODBUS Poll utility is used to read the values sent by the program over MODBUS communication. Another MODBUS TCP Client can be easily connected to a device configured by this way.
Overall, this article summarizes the features and advantages of MODBUS TCP Master and MODBUS TCP Slave communication protocols in Mikrodev PLC devices. Mikrodev MP110 and MP211 PLC Series offer significant benefits in industrial automation systems with their master and slave connection features in MODBUS TCP protocols. MODBUS is a well-established serial communication protocol that meets industrial communication needs with its simple and effective structure.
The PLC series provides a powerful communication infrastructure through MODBUS TCP Master and Slave blocks. In particular, the TCP Master block is used to read or assign values by activating the MODBUS TCP Master protocol at the physical interface via the communication port input. The activated protocol is finalized by connecting the request sending blocks to the MODBUS TCP Master block.
By means of that system, instant read or write requests are managed by intelligent mechanisms and the “MODBUS Slave” utility is used to view values or assign new values over the MODBUS communication protocol during online monitoring. These advantages of MODBUS TCP protocols in Mikrodev PLCs ensure a safe and efficient performance in industrial automation applications. Mikrodev PLC products work integrated with these protocols to provide reliable and efficient performance in industrial applications. Therefore users can develop flexible and optimized solutions in accordance with various industrial needs.