Understanding the Differences Between PLC, DCS & SCADA – A Selection Guide
In today’s industrial landscape, the selection of an appropriate control system architecture plays a pivotal role in ensuring optimal efficiency and effectiveness. Among the array of technologies available, Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs), Distributed Control Systems (DCS), and Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) systems stand out as pillars of industrial automation. Each offers distinct advantages and limitations tailored to specific applications. In this guide, we delve into the nuances of when to deploy PLCs, DCS, and SCADA systems, equipping you with insights to make well-informed decisions for your operational needs.
What are Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs)?
Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) are specialized industrial computers designed to control and automate manufacturing processes, machinery, and other electromechanical systems. They play a crucial role in industrial automation by monitoring inputs from sensors and other devices, executing control logic based on programmed instructions, and controlling outputs such as motors, valves, and actuators to achieve desired outcomes.
Key Features of PLCs
Speed and Determinism: PLCs excel in applications requiring fast response times and deterministic behavior. They are optimized for real-time control, making them ideal for systems where precise timing is crucial.
Modularity and Scalability: PLCs offer modular hardware configurations, allowing for easy expansion or modification of control systems as needed. This scalability makes them suitable for applications ranging from small-scale operations to large industrial plants.
Reliability: PLCs are known for their robustness and reliability in harsh industrial environments. They are often preferred for mission-critical applications where downtime must be minimized.
Ease of Programming: PLCs use ladder logic or other graphical programming languages that are intuitive for engineers and technicians familiar with electrical schematics. This simplifies system design and maintenance.
What Is Distributed Control Systems (DCS)?
Distributed Control Systems (DCS) are specialized control systems employed in large-scale industrial processes to centrally monitor and manage distributed assets and operations within a facility. Unlike standalone units like Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs), DCS utilizes a distributed architecture with centralized control rooms overseeing interconnected components such as controllers, input/output modules, and field devices spread throughout the plant. DCS systems offer scalability, redundancy, and advanced control algorithms, enabling operators to optimize processes, ensure regulatory compliance, and enhance efficiency in industries like chemical processing, oil and gas, power generation, and more.
Key Features of DCSs
Complex Processes: DCS excels in applications with complex control requirements, multiple process variables, and interconnected subsystems. It provides centralized monitoring and control of diverse processes across an entire plant.
Scalability and Integration: DCS architectures are highly scalable, making them suitable for large and complex industrial operations. They facilitate seamless integration of control, monitoring, and data management functions.
Redundancy and Fault Tolerance: DCS systems often incorporate redundancy at various levels to ensure high availability and fault tolerance. This is critical for maintaining continuous operation in industries where downtime can result in significant losses.
Advanced Control Algorithms: DCS platforms offer sophisticated control algorithms and optimization tools for process optimization, energy efficiency, and quality control. They enable operators to fine-tune processes for optimal performance.
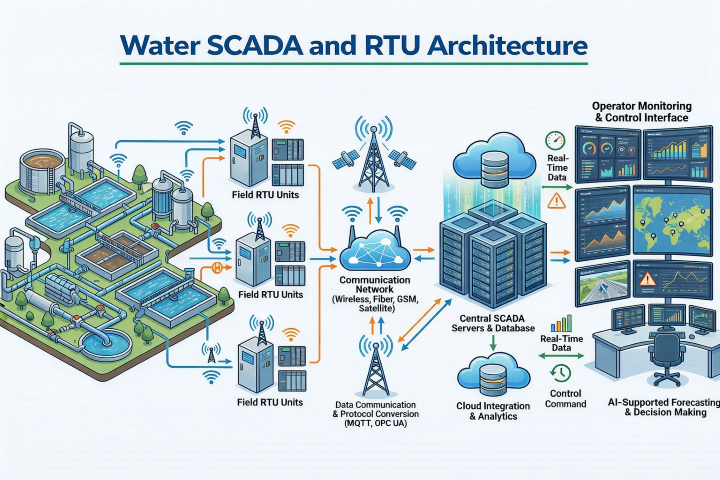
What Is Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) Systems?
Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) systems are comprehensive control systems used to remotely monitor and manage critical infrastructure and industrial processes in real-time. SCADA systems collect data from sensors, meters, and other devices distributed across a wide geographical area and present it to operators in a centralized interface for analysis and control. Unlike Distributed Control Systems (DCS), SCADA systems focus primarily on data acquisition, visualization, and remote control, making them ideal for applications such as utilities, transportation, telecommunications, and building management. SCADA systems offer features such as alarm management, historical data logging, and remote access, empowering operators to make informed decisions, detect anomalies, and respond promptly to operational issues for enhanced efficiency, safety, and reliability.
Key Features of SCADA Systems
Remote Monitoring and Control: SCADA systems are ideal for applications where monitoring and control of geographically dispersed assets are required. They allow operators to remotely access and manage equipment from a central location.
Data Acquisition and Visualization: SCADA systems collect data from sensors and devices across the network and present it in a graphical user interface. This data visualization enables operators to monitor trends, detect anomalies, and make informed decisions in real-time.
Alarm Management: SCADA systems provide robust alarm management capabilities, allowing operators to set thresholds and receive notifications for abnormal conditions. This helps in early detection of potential issues and proactive intervention to prevent downtime or safety hazards.
Historical Data Analysis: SCADA systems store historical data for trend analysis, performance monitoring, and regulatory compliance. This data can be used for troubleshooting, optimization, and reporting purposes.
Learn more about SCADA: What is SCADA, Who Uses It and How It Works
Selection Guide: Making the Right Choice
When selecting between PLCs, DCS, and SCADA systems, consider the following factors:
– Nature of the Process
Determine the complexity, scale, and criticality of the process being controlled.
– Control Requirements
Evaluate the need for discrete control, process control, or remote monitoring and data acquisition.
– Scalability
Assess the potential for future expansion and integration with other systems.
– Reliability and Redundancy
Consider the level of reliability and fault tolerance required for uninterrupted operation.
– Ease of Use and Maintenance
Take into account the ease of programming, configuration, and ongoing maintenance.
– Cost Considerations
Compare upfront costs, lifecycle expenses, and return on investment for each option.
By carefully analyzing these factors and understanding the strengths and limitations of PLCs, DCS, and SCADA systems, you can make an informed decision that best aligns with your industrial automation needs. Whether you’re managing a small manufacturing operation or a large-scale industrial plant, choosing the right control system architecture is essential for optimizing efficiency, productivity, and safety.
Conclusion
In the dynamic landscape of industrial automation, the choice between Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs), Distributed Control Systems (DCS), and Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) systems is pivotal. Each technology offers distinct advantages suited to particular applications, and understanding their strengths and weaknesses is essential for selecting the optimal solution.
PLCs stand out for their speed, determinism, and reliability, making them ideal for discrete control tasks in manufacturing environments. DCS excels in managing complex industrial processes with centralized control, scalability, and advanced optimization capabilities. SCADA systems shine in remote monitoring, data acquisition, and visualization, enabling operators to oversee distributed assets from a centralized location.
When making decisions about control system architecture, it’s crucial to consider factors such as the nature of the process, control requirements, scalability, reliability, ease of use, and cost considerations. By carefully evaluating these factors and understanding the unique features of each technology, industrial organizations can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and business objectives.
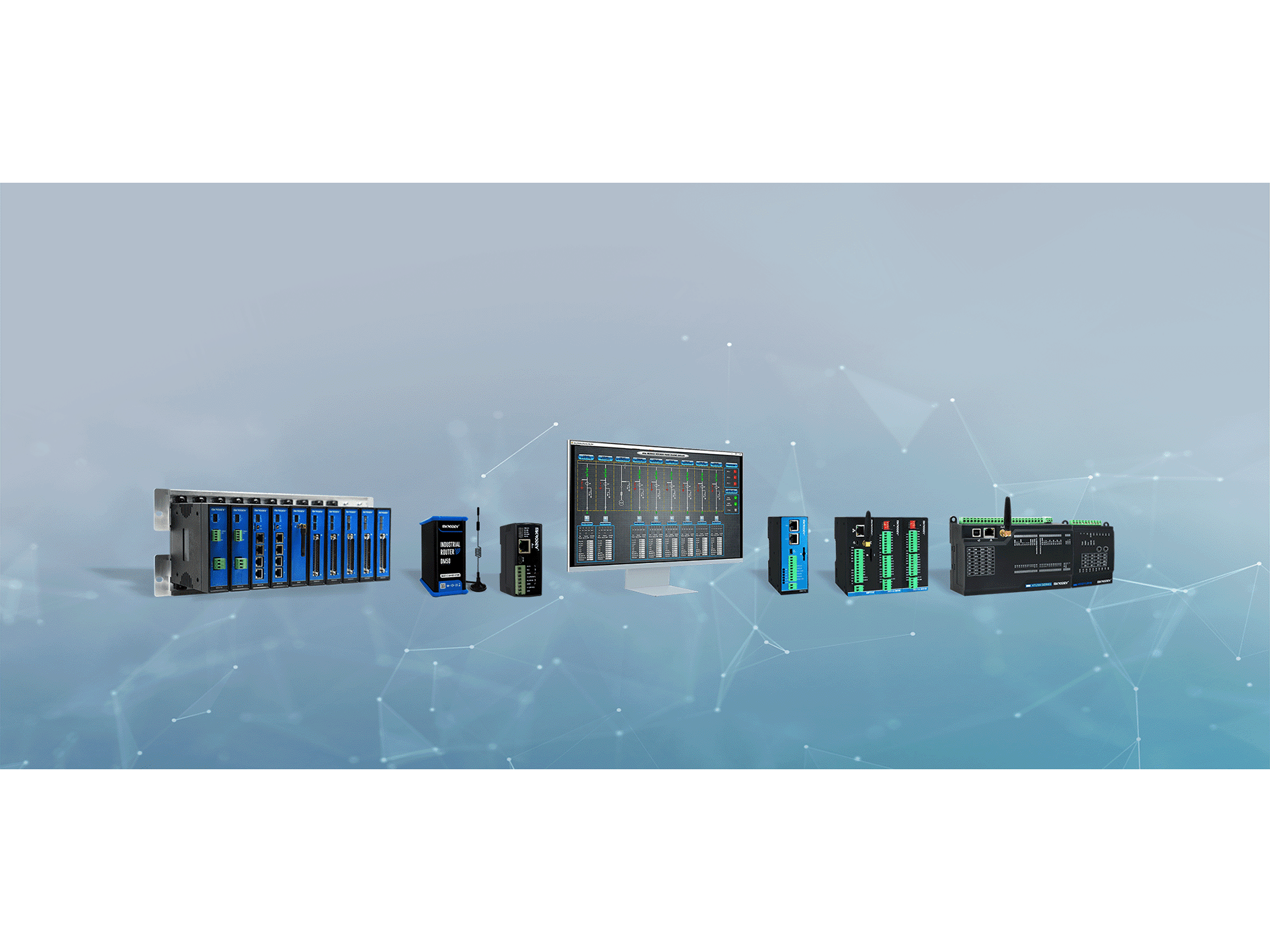
In this context, Mikrodev emerges as a noteworthy player, offering innovative solutions in industrial automation. With a commitment to excellence, Mikrodev provides cutting-edge PLCs, DCS, and SCADA systems tailored to the specific requirements of diverse industries. Their comprehensive product portfolio, coupled with expertise in system integration and support services, positions them as a trusted partner for businesses seeking to optimize their automation processes.
Ultimately, whether you’re managing a small-scale operation or a large industrial plant, choosing the right control system architecture is essential for maximizing efficiency, productivity and safety. By leveraging the capabilities of PLCs, DCS, SCADA systems, and the expertise of industry leaders like Mikrodev, organizations can embark on a journey towards enhanced performance, competitiveness, and sustainability in the ever-evolving landscape of industrial automation.