Understanding the Essence of Industrial Automation
In the dynamic landscape of modern industries, the concept of industrial automation has emerged as a fundamental driver of efficiency, precision, and progress. As industries continue to evolve and expand, the need for streamlining processes, enhancing productivity, and minimizing errors becomes increasingly vital. This is where industrial automation steps in, playing a pivotal role in revolutionizing the way industries function.
What is Industrial Automation?
Industrial automation can be defined as the use of computerized systems, software, and devices to control and monitor industrial processes, machines, and equipment. At its core, industrial automation refers to the integration of various control systems and technologies to operate machinery and processes in manufacturing and other industrial sectors with minimal human intervention. It embodies the marriage of cutting-edge technologies with systematic methodologies to achieve superior results. Industrial automation aims to improve the efficiency, quality, safety, and reliability of industrial operations, as well as reduce costs, waste, and human errors.
Industrial automation can be applied to various sectors and domains, such as manufacturing, transportation, energy, water treatment, building management, and more.
Some of the benefits of industrial automation include:
- Increased productivity and output: Industrial automation can enable faster and more consistent production cycles, as well as optimize the use of resources and materials.
- Enhanced quality and accuracy: Industrial automation technologies can reduce the variability and defects in products and services, as well as ensure compliance with standards and regulations.
- Improved safety and security: Industrial automation systems can protect workers from hazardous environments and tasks, as well as prevent unauthorized access and tampering with critical systems and data.
- Reduced operational costs: Industrial automation systems can lower the labor, maintenance, and energy costs associated with industrial processes, as well as minimize downtime and waste.
Industrial automation relies on various technologies and components, such as:
- Sensors and actuators: These are devices that measure and control physical parameters, such as temperature, pressure, flow, level, position, speed, force, etc.
- Programmable logic controllers (PLCs): These are specialized computers that execute logic programs to control industrial processes and equipment. PLCs can communicate with sensors, actuators, human-machine interfaces (HMIs), and other devices via input/output (I/O) modules.
- Human-machine interfaces (HMIs): These are devices that allow operators to interact with industrial systems and equipment, such as displays, keyboards, touchscreens, etc.
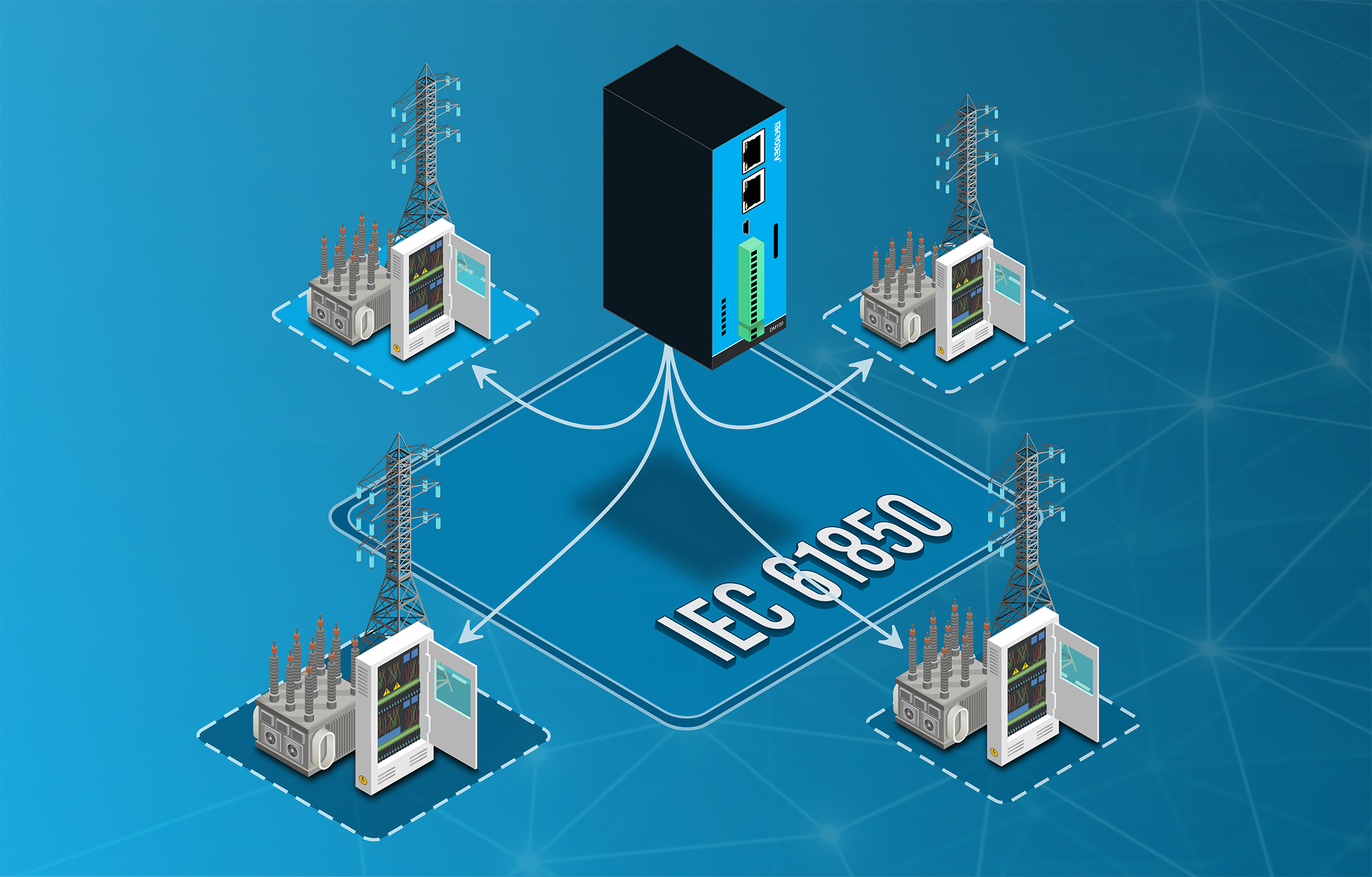
- Supervisory control and data acquisition (SCADA) systems: These are software applications that collect, process, and display data from industrial systems and equipment, as well as provide remote control and supervision functions. SCADA systems can communicate with PLCs, HMIs and other devices via communication networks.
- Communication networks: These are the mediums that enable data transmission between industrial devices and systems, such as wired or wireless networks, protocols, and standards.
Main Types of Industrial Automation Technologies
PLC Automation: Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) are the unsung heroes of industrial automation. They are rugged and versatile digital computers that control a range of applications from simple lighting functions to complex industrial processes. PLCs automate tasks that require high-speed operations, accurate sequencing, and robust performance.
SCADA Automation: Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) systems offer a comprehensive view of industrial processes. They collect real-time data from multiple locations, monitor processes, and provide the means to control them. SCADA automation systems have found applications in various industries, including building automation, wastewater treatment plants, and transportation.
Vessel Automation: In the maritime industry, vessel automation has transformed the way ships are operated and managed. From navigation and engine control to cargo handling, vessel automation enhances safety, efficiency, and crew management.
Rail Automation Solutions: Rail automation is a game-changer for the transportation sector. Automated train control, signaling, and communication systems have not only improved safety but also increased the capacity and reliability of rail networks.
Industrial Process Automation: This involves using advanced technologies to automate industrial processes, thereby increasing efficiency, reducing costs, and ensuring consistency. Industrial process automation systems streamline workflows, optimize resource utilization, and improve overall productivity.
The Role of Expansion Modules in Automation: Programmable automation expansion modules act as building blocks for automation systems. They enhance the functionality of devices and enable the customization of automation solutions to suit specific needs.
Industrial Automation in Various Sectors
Energy: Industrial automation technologies play a critical role in optimizing energy consumption and managing power grids. They enable real-time monitoring and control of energy distribution networks.
Transportation: Automation has revolutionized the transportation sector, from self-driving cars to automated warehouses. Advanced automation has improved the safety and efficiency of transportation systems.
Wastewater Treatment Plants: Automation is transforming wastewater treatment processes by enabling remote monitoring, predictive maintenance, and efficient resource utilization. This contributes to the conservation of water resources and minimizes environmental impact.
Building Automation: Building automation SCADA systems oversee various building functions, including HVAC, lighting, security, and fire safety. These systems ensure comfort, safety, and energy efficiency in commercial and residential spaces.
Campus Automation: Beyond the industrial realm, campus automation is reshaping educational institutions. From monitoring security systems and managing energy consumption to enhancing communication networks, campus automation ensures a seamless and secure environment for students and staff.
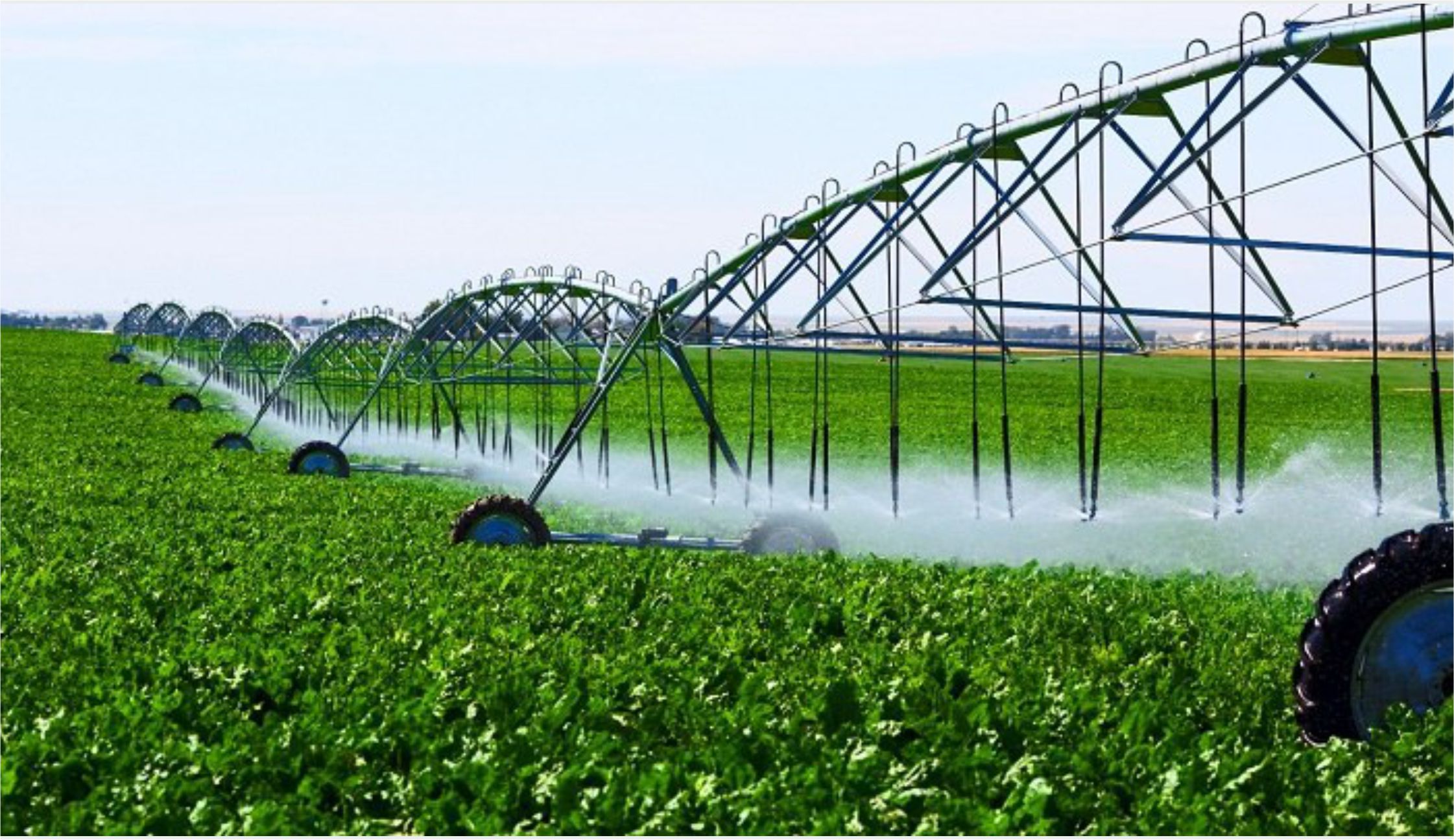
Agricultural Automation Systems: In the realm of agriculture, automation is optimizing crop cultivation and livestock management. Automated irrigation systems, precision agriculture technologies, and robotic assistance are revolutionizing traditional farming practices, leading to increased yields and sustainable resource management.
As it is seen industrial automation is a key driver of innovation and competitiveness in various industries. By adopting industrial automation technologies and solutions, industries can improve their productivity, quality, safety, and profitability.
Because industrial automation is a rapidly evolving field, it incorporates new technologies and innovations to meet the changing needs and challenges of various industries. Some of the emerging trends and developments in industrial automation may include such as :
- Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML): These are technologies that enable machines to learn from data and perform tasks that require human intelligence or skills. AI and ML can enhance the capabilities and performance of industrial systems and equipment by providing predictive analytics, anomaly detection, optimization, decision support, etc.
- Internet of Things (IoT) and cloud computing: These are technologies that enable the interconnection and data sharing between physical objects and digital platforms via the Internet. IoT and cloud computing can enable the remote monitoring and control of industrial systems and equipment by providing real-time data access, storage, and processing.
- Cybersecurity: This is the practice of protecting industrial systems and equipment from cyberattacks or threats that can compromise their functionality or integrity. Cybersecurity can ensure the confidentiality, availability, and integrity of industrial data and processes by providing encryption, authentication, authorization, etc.
To summarize industrial automation technology is the cornerstone of modern industry, driving efficiency, precision, and innovation across sectors. The integration of technologies like PLC automation (automation with programmable logic controllers in other words), SCADA systems, and expansion modules has reshaped the industrial landscape, paving the way for increased productivity and reduced human error. With the relentless advancement of technology, the future of industrial automation holds the promise of even greater transformation and optimization. Whether it’s vessel automation, rail automation solutions, or automation in manufacturing, energy, and transportation, the impact of automation is undeniable. It is a journey toward a more efficient, sustainable, and connected industrial ecosystem.
Mikrodev provides powerful tools and devices for industrial automation technologies. Please check our product range for Distributed Control Systems (DCS), Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs), IoT Protocol Converters, and Operator Control & Monitoring System (SCADA systems) as well as Expansion Modules and more to improve the efficiency, productivity, quality, and safety of your industrial automation processes and systems. As global technology continues to evolve, Mikrodev’s R&D efforts and investments expand accordingly to provide a smooth transition of industrial automation products and software