In the rapidly evolving landscape of industrial automation, the integration of Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) and communication protocols holds vital importance. The aim of this article is to provide information on how to use MODBUS Gateway in PLC programming, enabling a seamless
PLCs: The Central Control Point of Industrial Automation
PLCs are control-focused units commonly used in industrial enterprises, manufacturing facilities, and automation systems. They function as the central nervous system of a facility, coordinating processes like data collection, analysis, decision-making, and control, forming the foundation of industrial operations.
MODBUS Protocols: Fundamental Communication Information

Modbus is a communication protocol extensively used in industrial automation systems. It finds broad application in factory automation, the energy sector, transportation systems, and various other industrial domains.
Modbus typically allows a main device (such as a computer or a controller) to communicate with multiple devices (such as sensors, motors, actuators). The Modbus protocol typically relies on a client/server model. The client is a device requesting data or sending commands, while the server responds to these requests or processes the commands.
This protocol is generally used in two different physical communication modes: Modbus RTU (Remote Terminal Unit) and Modbus TCP/IP.
MODBUS TCP: Ethernet Data Transfer
MODBUS TCP is a variant of the MODBUS protocol that operates in high-speed communication Ethernet networks, utilizing the TCP/IP network protocol. Data packets are transported via TCP/IP and are commonly used in industrial networks.
MODBUS RTU: Serial Communication Technology
In contrast to MODBUS TCP, MODBUS RTU is designed for serial communication and is an ideal choice for applications where Ethernet connections might be challenging. Data is usually packaged over serial communication tools like RS-485 or RS-232 and transmitted between devices.
MODBUS Gateway: Bridging Different Protocols
The MODBUS Gateway is an important tool facilitating communication between different industrial devices. For instance, it acts as a bridge, enabling data exchange between Modbus TCP/IP and Modbus RTU, connecting different devices through correct connection points to establish seamless communication.
Application Strategies: Integration of MODBUS Gateway with PLCs
The integration of Modbus Gateway with PLCs involves steps such as selecting appropriate devices, establishing connections, determining configuration settings, and testing data exchange. These steps are crucial to facilitate communication between different devices and ensure successful integration.
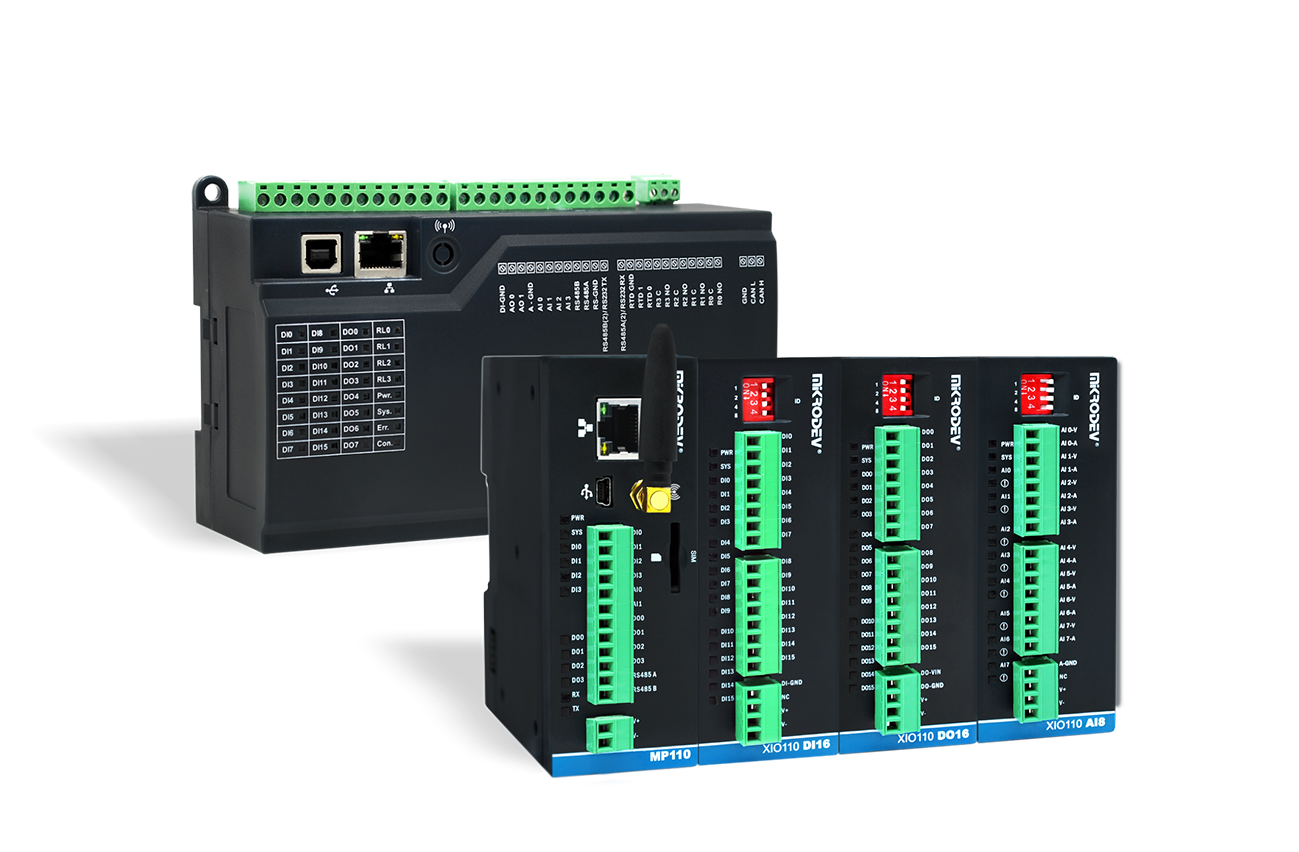
MODBUS Gateway in Mikrodev PLCs:
Mikrodev control devices can be programmed to work simultaneously as Gateways among the supported protocols. One of the blocks facilitating this is the Modbus Gateway block.
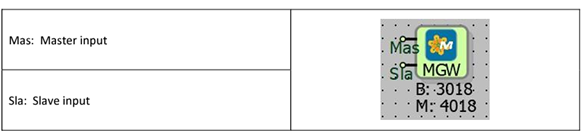
The Modbus Gateway block can provide services in two directions as listed below.
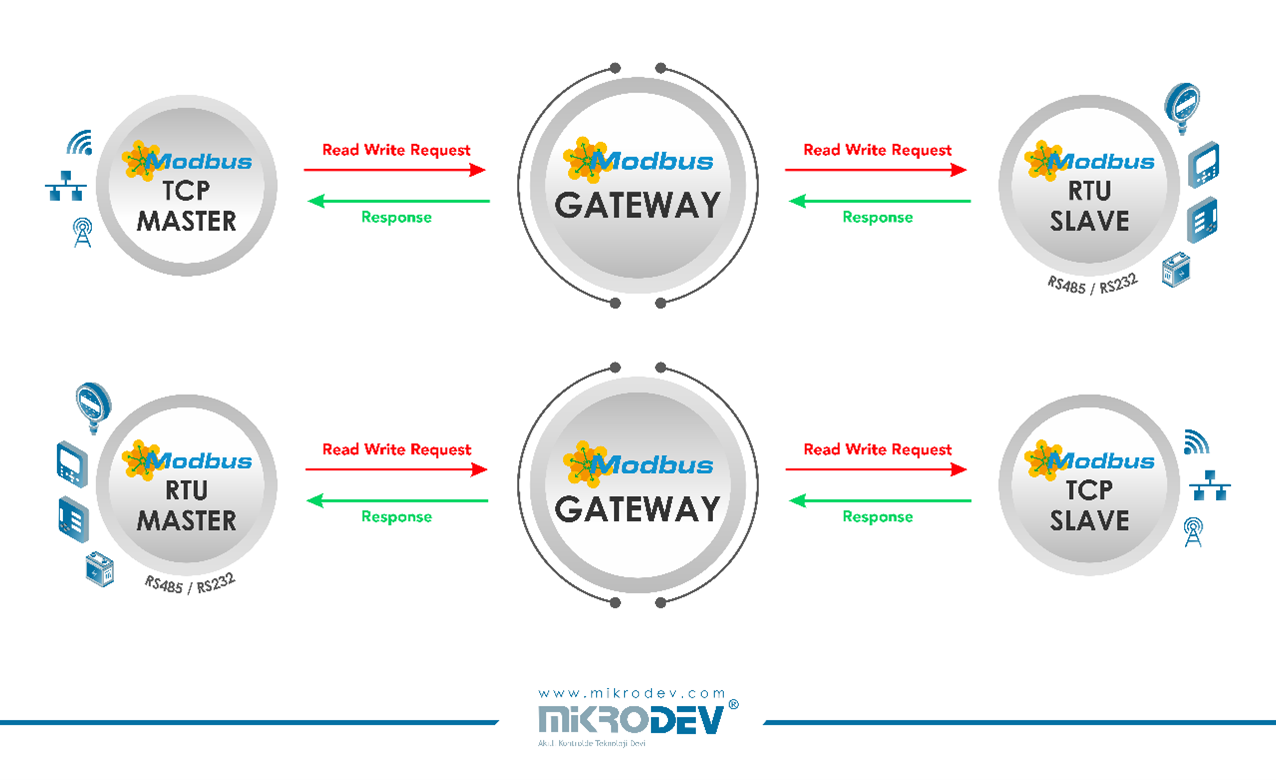
Connecting the Master and Slave blocks is sufficient for the Gateway to start working. If a request comes from a different ID than the Modbus ID on the Slave block, the relevant request will be read through the Master block.
· Sample Application:
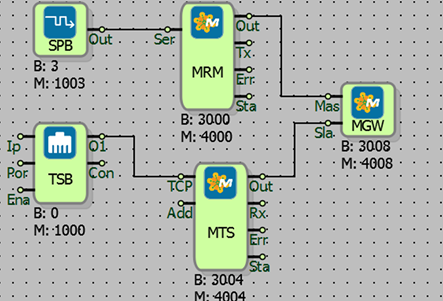
In this example, the Modbus Gateway block is used to create a gateway for Modbus RTU Master block to access Modbus TCP Slave block. The output of the Modbus RTU Master block is connected to the “Efe” input of the Modbus Gateway block, and the output of the Modbus TCP Slave block is connected to the “Sla” input. Request packets received over Modbus RTU are converted into TCP packets and sent to the TCP network. The response received from the TCP network is then sent back to the Modbus RTU network.
Case Studies: Real-World Applications of MODBUS Gateway in PLC Programming
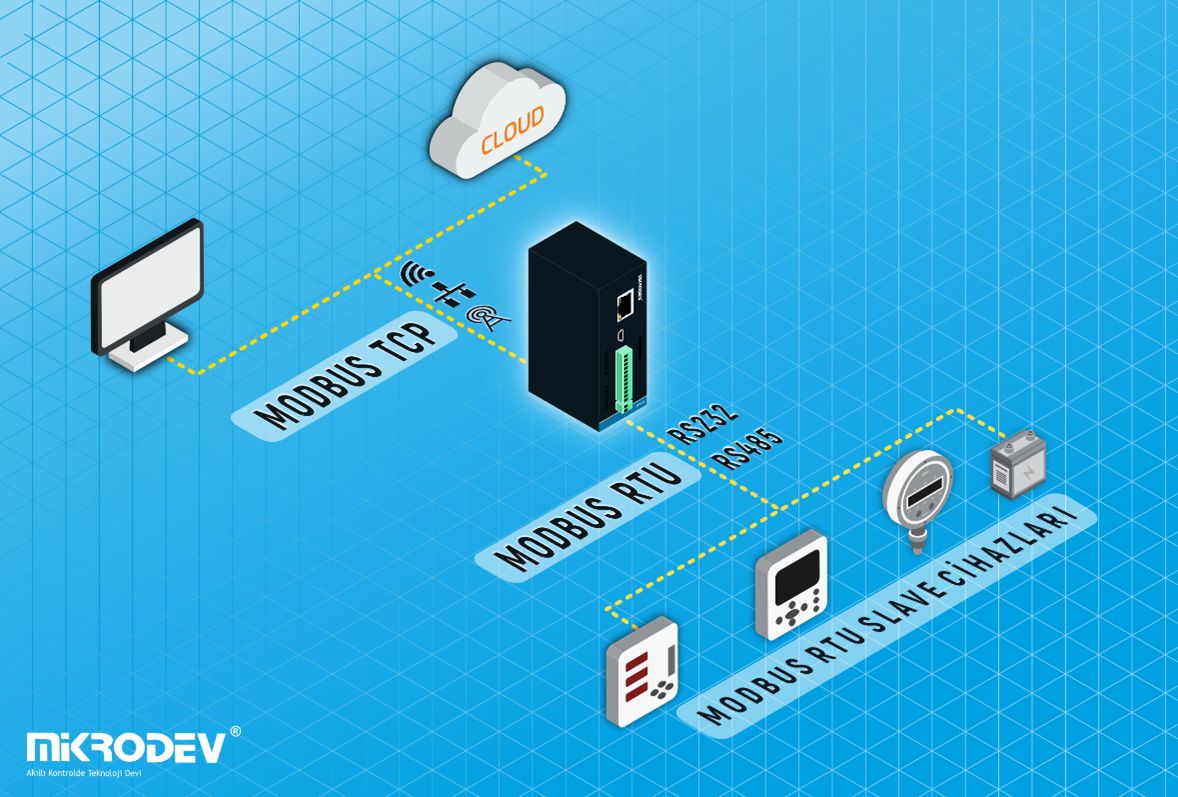
Energy monitoring systems used in areas such as buildings or industrial facilities help track and manage energy consumption. These systems often work in integration with various energy measurement devices, smart meters, or sensors. The use of different communication protocols by different devices can complicate data exchange. Here is where the use of MODBUS Gateway comes into play:
For instance, you have an energy meter using Modbus TCP/IP protocol integrated into an energy monitoring system in a building and a temperature sensor using a different serial communication protocol. You aim to integrate the data from these two devices into a central control system or monitoring panel.
In this scenario, the MODBUS Gateway takes data from the energy meter using Modbus TCP/IP and combines it with the data from the temperature sensor using a different protocol, creating usable data for reporting or analysis through a central control or monitoring system.
This way, the MODBUS Gateway facilitates data exchange between different protocols in energy monitoring systems, enabling the aggregation and analysis of energy consumption data. This, in turn, can assist in improving energy efficiency, reporting, and decision-making processes.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the MODBUS Gateway facilitates efficient and reliable communication between different devices by enabling integration with PLCs, a cornerstone of industrial automation. This contributes to increasing the efficiency of industrial processes and aids in more effective management of systems.